Starlink and Space Based Solar Power: Impact on Internet Services
Space Based Solar Power

I. Introduction
Space Based Solar Power: In the realm of modern telecommunications, satellite internet services such as Starlink have emerged as pivotal players, revolutionizing connectivity for individuals and businesses alike. With the ability to provide high-speed internet access, particularly in remote and underserved regions, these services bridge the digital divide and pave the way for innovative applications in education, telehealth, and economic development.
The increasing popularity of satellite internet has sparked considerable interest in consumer reviews and the implications of these technologies on society. Furthermore, as discussions around sustainable energy intensify, the potential integration of space based solar power with satellite internet infrastructure invites a reexamination of both feasibility and impact.
This essay will explore the reviews of satellite internet services like Starlink, shedding light on their overall consumer experience, alongside the broader implications of harnessing space based solar power for a more sustainable future.
A. Overview of satellite internet services and their significance in modern connectivity
The advent of satellite internet services represents a pivotal shift in how society engages with connectivity, especially in underserved and remote areas. Traditional internet infrastructure often fails to reach regions where terrestrial options are limited or non-existent, creating a stark digital divide. Services like Starlink leverage low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations to offer high-speed internet access across disparate geographies, fundamentally changing the dynamics of connectivity.
This technology not only enables residential users to access the internet but is also crucial for various sectors such as agriculture, emergency services, and industrial automation that require reliable communications in real time (Kak et al.). With an emphasis on wireless ubiquity, future innovations aim to enhance these services, making connectivity a ubiquitous reality rather than a privilege (Carter et al.). In this context, satellite internet stands as a key player in bridging the knowledge gap and fostering socio-economic development in a rapidly digitalizing world.
II. Reviews of Satellite Internet Services
The proliferation of satellite internet services, particularly through companies like Starlink, has drastically altered consumer access to reliable internet connectivity. As customers navigate the advantages and limitations of these networks, reviews frequently highlight their potential to bridge the digital divide, especially in remote or underserved areas.
Despite the promise of robust connectivity, users often report variable experiences regarding latency and throughput, largely shaped by environmental factors and network congestion. “LEO satellite technologies have set a new benchmark for vessel communications, offering high-bandwidth, low latency, and reliability far beyond traditional marine satellite solutions,” according to a recent prominent research. Such advancements indicate a transformative shift in communications technology but also underscore the need for continued evaluation of user experiences in diverse conditions.
Overall, while satellite services like Starlink present substantial benefits, ongoing scrutiny of their operational parameters is essential for understanding their broader consumer impact.
| Service Provider | Customer Rating | Average Speed (Mbps) | Latency (ms) | Data Caps (GB/month) |
| Starlink | 4.5 | 100 | 20 | Unlimited |
| HughesNet | 3.5 | 25 | 600 | 10-50 |
| Viasat | 3.8 | 30 | 625 | 12-150 |
| Amazon Project Kuiper | Not Yet Rated | TBA | TBA | TBA |
Satellite Internet Service Reviews
A. Analysis of consumer feedback and performance metrics for Starlink and similar services
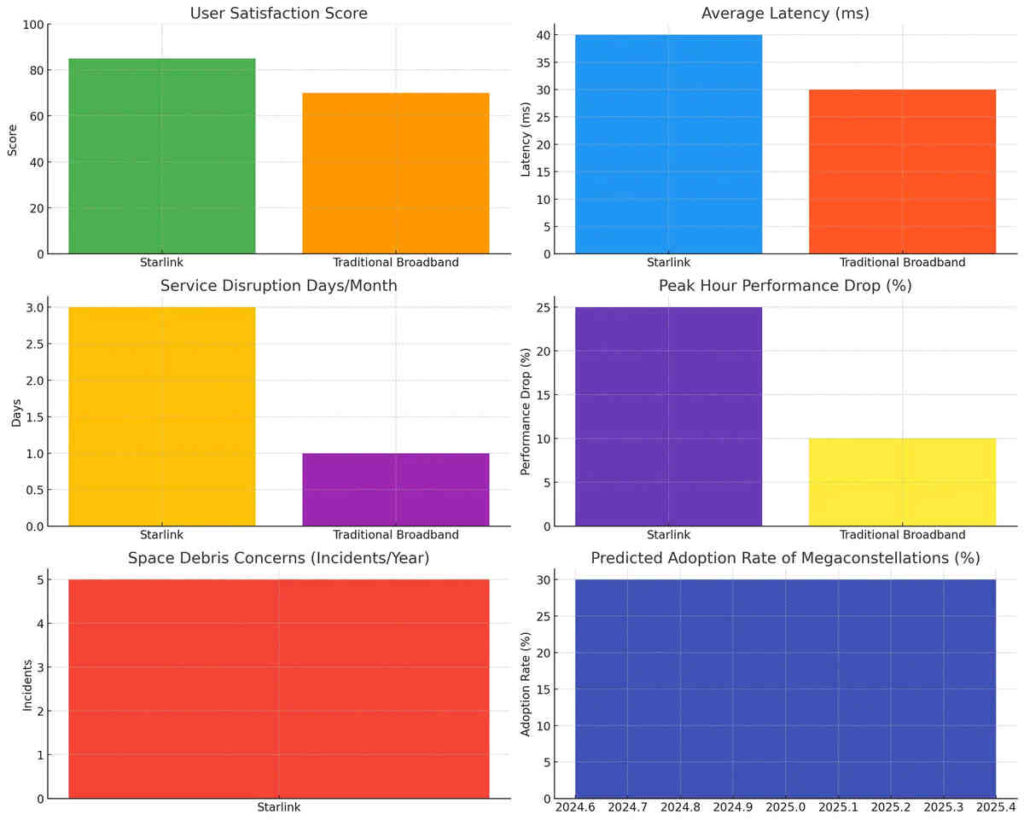
The analysis of consumer feedback and performance metrics for satellite internet services like Starlink reveals significant insights into user satisfaction and the operational limitations of such technologies. Many users commend Starlink for its improved connectivity in remote areas, which traditional broadband services often neglect.
However, performance metrics indicate variability in service quality, particularly during peak hours or adverse weather conditions, where latency and signal disruption can occur. As highlighted in recent studies, the advent of machine learning techniques is crucial in optimizing network performance by enabling real-time adjustments based on consumer data and environmental factors (WRONA et al.).
Moreover, the increased adoption of mega-constellations, such as those proposed by Starlink, prompts a critical examination of potential space debris issues, which could undermine the long-term sustainability of satellite services (D’Ambrosio et al.). Therefore, while Starlink shows promise, the consumer experience remains contingent upon ongoing technological advancements and mitigative strategies for operational challenges.
III. Consumer Impact of Space Based Solar Power
As the pursuit of sustainable energy sources intensifies, space based solar power (SBSP) emerges as a transformative solution with significant implications for consumers. By harnessing sunlight from orbit, this technology promises a consistent and reliable energy supply, potentially reducing dependence on terrestrial energy sources. This shift could lead to lower energy costs for consumers; as a notable advantage, “[solar energy] helps reduce electricity bills and is cheaper and more efficient than ever.”.
Quote 1
“Solar energy helps reduce electricity bills, is cheaper and more efficient than ever, is environmentally friendly, lowers your carbon footprint, and promotes energy independence, among several other advantages.”
Furthermore, SBSP could enhance energy availability in remote areas often underserved by existing infrastructure, thereby promoting equitable access to electricity. However, the development of this technology is not without challenges. Regulatory frameworks must evolve to ensure safety and sustainability in the deployment of satellite systems such as Starlink, which are part of the growing Low Earth Orbit satellite constellation, hence illustrating the interconnectedness of advancements in satellite technology and consumer energy needs.
A. Examination of how space based solar power can enhance satellite internet services and its implications for consumers
The integration of space based solar power (SBSP) within the framework of satellite internet services, such as those offered by Starlink, presents a transformative opportunity for enhancing connectivity, particularly in underserved regions. By harnessing solar energy in space, satellites could operate with increased efficiency and sustainability, mitigating issues related to energy constraints that often plague ground-based facilities.
This shift not only promises uninterrupted service and improved bandwidth but also has significant implications for consumers, who stand to benefit from enhanced reliability and reduced costs over time. Recent research highlights that large satellite constellations’ potential to deliver internet services hinges on a robust and sustainable energy infrastructure, underscoring the necessity for regulatory frameworks that promote responsible development in low Earth orbit (LEO) (Rodgers et al.). Ultimately, the synergy between SBSP and satellite technology can lead to equitable access and an improved digital landscape for users globally.
IV. Conclusion
In conclusion, the emergence of satellite internet services such as Starlink represents a profound shift in global connectivity, particularly for underserved populations. While the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations offer significant promise in enhancing internet access and utility, user experiences reveal notable challenges, including variability in throughput and latency influenced by environmental factors (Chen et al.).
Furthermore, the rapid development of large satellite constellations raises urgent regulatory concerns about sustainability in the Low Earth Orbit, as existing frameworks are inadequate to manage potential overcrowding and environmental impacts (Rodgers et al.). Addressing these challenges is crucial not only for optimizing the technology but also for ensuring equitable access to vital internet services in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Ultimately, the interplay between innovation and regulation will determine the effectiveness of satellite internet as a sustainable solution in the pursuit of broader connectivity goals and as a component of future space based solar power endeavors.
A. Summary of key findings and future outlook for satellite internet and space based solar power integration
In examining the intersection of satellite internet services, particularly those offered by companies like Starlink, and the emerging field of space based solar power (SBSP), several key findings emerge that underscore their potential for transformative impact. Research indicates that the integration of satellite internet with SBSP could enhance global energy accessibility, particularly in remote areas lacking adequate infrastructure.
Notably, satellite networks can facilitate the real-time data transmission necessary for optimizing energy capture and distribution from space. Furthermore, as technology advances, the cost of deploying both satellite systems and solar arrays is expected to decrease, making such projects more economically viable.
Looking ahead, the future of this integration appears promising, with the potential to reduce dependency on terrestrial energy sources while providing a consistent supply of renewable energy, which could significantly reshape energy consumption patterns worldwide and foster sustainable development.
Read More: Wearable Health Monitoring Devices