Biometric Authentication Technology: Identity Verification

Biometric Authentication Technology In today’s rapidly advancing digital landscape, ensuring robust and trustworthy identity verification biometrics mechanisms has become more crucial than ever before. With the advent of biometric authentication, a revolutionary technology that relies on distinct physical or behavioral traits to accurately identify individuals, a new era of secure verification has emerged.
This article delves into the immense potential of Biometric Authentication Technology, shedding light on its versatile applications spanning across diverse industries. Join us on this captivating journey as we explore the transformative influence of biometrics and its pivotal role in shaping the future of identity verification. Brace yourself for an enlightening exploration into the captivating realm of biometrics and its profound impact on the world of digital security.
No 1: The Basics of Biometric Authentication Technology:

In the realm of modern security systems, biometric authentication stands at the forefront, revolutionizing the way we verify identities. This comprehensive article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the basics of biometric authentication, empowering readers with valuable insights into its fundamental principles and functionalities.
Delving into the world of biometrics
We will explore a myriad of distinctive modalities that contribute to the success of Biometric Authentication Technology. From ubiquitous fingerprint recognition to increasingly sophisticated facial recognition technology, iris scans, voice recognition, and beyond, we will unravel the diverse range of biometric identifiers employed to establish a foolproof identification system.
Furthermore
This article will shed light on the differentiating factors that set biometrics apart from traditional authentication methods like passwords and PINs. By examining the inherent strengths and limitations of biometric authentication, we can also gain a deeper appreciation for its unparalleled accuracy, convenience, and resistance to forgery.

Join us on this captivating journey as we demystify the fascinating world of biometric authentication, providing you with a robust foundation to comprehend its significance in the realm of digital security. Prepare to be captivated by the limitless potential of biometrics and the transformative impact it holds in safeguarding our identities.
No 2: Advantages and Challenges of Biometric Authentication Technology:
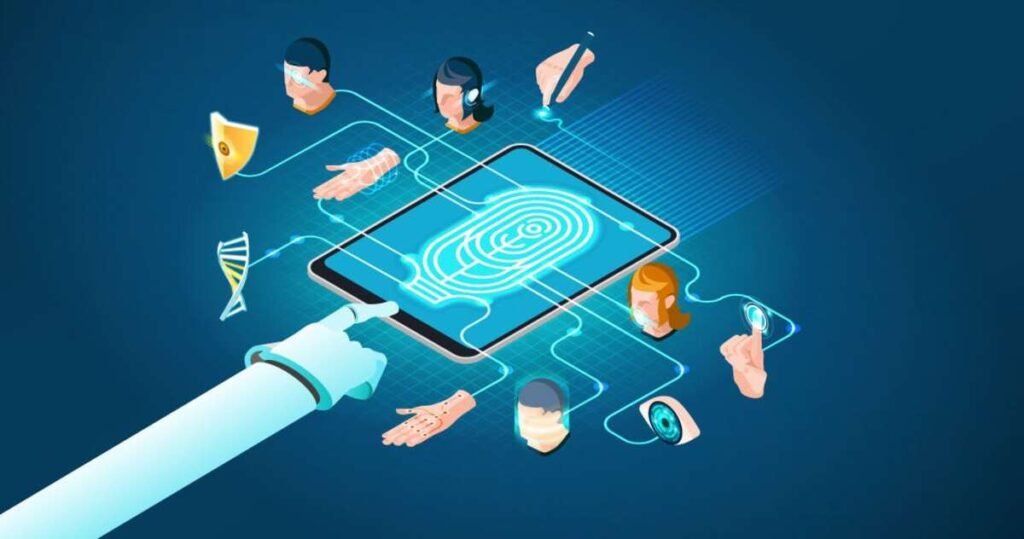
In an era where most secure biometric authentication and seamless authentication is paramount, Biometric Authentication Technology emerges as a game-changing solution, boasting inherent advantages that redefine the way we verify identities. This article aims to explore the remarkable benefits of biometric authentication, while also addressing the potential challenges it presents.
One of the key advantages of biometric authentication lies in its heightened security. Unlike traditional methods such as passwords or PINs, biometrics relies on unique physical or behavioral traits that are inherently difficult to replicate. This makes it significantly more challenging for unauthorized individuals to gain access, enhancing overall security levels. Additionally, biometric data is typically stored in encrypted formats, further fortifying the protection of sensitive information.
Biometric authentication also offers unparalleled convenience. With the integration of biometric sensors in modern devices, individuals can effortlessly verify their identities with a simple touch, glance, or voice command. Gone are the days of remembering complex passwords or carrying multiple identification cards. Biometrics provides a user-friendly experience that not only saves time but also reduces the frustration associated with forgotten passwords or lost cards.
However, alongside these advantages, Biometric Authentication Technology presents certain challenges that warrant consideration. Privacy concerns arise due to the collection and storage of personal biometric data. Individuals may worry about the potential misuse or unauthorized access to their unique identifiers. Safeguarding biometric information through robust encryption, stringent data protection measures, and transparent privacy policies becomes imperative to address these concerns effectively.
Furthermore, vulnerabilities can emerge in biometric systems. While highly accurate, certain factors like changes in appearance, injuries, or aging may affect the reliability of biometric data. Additionally, the possibility of spoofing or falsifying biometric identifiers exists, albeit with significant difficulty. These challenges necessitate continuous research and advancements in biometric technology to mitigate vulnerabilities and ensure its continued effectiveness.
No 3: Biometrics in Everyday Life: Revolutionizing Security and Efficiency
In today’s fast-paced world, Biometric Authentication Technology has emerged as a transformative technology, revolutionizing various aspects of our daily lives. This article delves into the widespread impact of biometrics, exploring its role in Smartphone security, financial transactions, access control systems, e-commerce platforms, healthcare, border control, and the transportation sector. Join us as we uncover how biometrics is reshaping the way we authenticate, enhancing security and efficiency in everyday activities.
Smartphone Security Biometric Authentication Technology:
Biometric Authentication Technology has become a cornerstone of Smartphone security. With features like fingerprint sensors, facial recognition, and iris scans, smartphones now offer seamless and robust protection. Users can also unlock their devices, authorize transactions, and access sensitive data with a simple touch or glance, replacing traditional passcodes and patterns. This integration of biometrics ensures personalized and highly secure Smartphone experiences.

Financial Transactions:
Biometrics has revolutionized the way we conduct financial transactions. Instead of relying solely on passwords or PINs, users can also now authorize payments using their fingerprints, facial scans, or voice recognition. This not only enhances security but also streamlines the checkout process, reducing friction and providing a seamless user experience. Biometric Authentication Technology is paving the way for more convenient and secure financial interactions.
Access Control Systems:
From corporate environments to residential buildings, access control systems are being fortified with biometric authentication. Biometrics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or palm scans replace traditional key cards or access codes, ensuring that only authorized individuals can enter restricted areas. This technology enhances security, eliminates the risk of lost or stolen credentials, and simplifies the access management process.
E-commerce Platforms:
Biometric Authentication Technology is transforming e-commerce platforms, enhancing security while streamlining user experiences. By utilizing biometric identifiers, such as fingerprints or facial scans, users can securely log in, authorize transactions, and validate their identities during online purchases. This frictionless authentication process reduces checkout times, builds trust, and provides a hassle-free online shopping experience.
Healthcare Sector:
Biometrics plays a vital role in the healthcare sector, safeguarding sensitive patient information and streamlining processes. Most secure biometric authentication access to electronic medical records, preventing unauthorized individuals from obtaining personal health data. It also enables healthcare providers to accurately identify patients, reducing medical errors and enhancing patient safety.
Border Control:
Border control agencies worldwide are adopting biometrics to strengthen security and expedite immigration processes. Facial recognition, iris scans, and fingerprint matching systems enable fast and accurate identification of travelers, enhancing border control efficiency. Biometrics streamline check boarding, and customs procedures, providing a seamless and secure travel experience.
Transportation Sector:
Biometrics is revolutionizing the transportation sector by improving passenger experiences and enhancing security. Airports and airlines are implementing biometric systems for self-check-in, automated security checks, and frictionless boarding processes. By utilizing facial recognition or fingerprint authentication, passengers can also navigate through various stages of travel swiftly and securely.
As Biometric Authentication Technology continues to evolve, addressing privacy concerns and vulnerabilities remains crucial. Safeguarding biometric data, implementing stringent security measures, and ensuring transparent privacy policies are paramount to maintaining trust and protecting individuals’ privacy.
No 4: Biometrics and Cyber security: Fortifying Digital Defenses

In an era of increasing digital threats, Biometric Authentication Technology has emerged as a powerful tool for strengthening cyber security measures. This article explores the pivotal role of biometrics in preventing identity theft, fraud, and data breaches. We delve into the ways biometric authentication enhances security, the role it plays in safeguarding sensitive information, and the techniques employed to protect biometric data from unauthorized access.
Biometric authentication offers a robust defense against identity theft, fraud, and unauthorized access. Unlike traditional authentication methods such as passwords or PINs, biometrics relies on unique physical or behavioral traits that are incredibly difficult to replicate. Whether fingerprint recognition, facial scans, or iris scans, biometrics provide a high level of accuracy in identifying individuals. Minimizing the risk of impersonation and unauthorized access.
By incorporating Biometric Authentication Technology into cyber security frameworks, organizations can establish multi-factor authentication systems than that significantly bolster security. Combining biometric identifiers with other factors like passwords or tokens creates a layered defense, making it substantially more challenging for attackers to bypass security measures.
Biometric Authentication Technology
Biometric authentication also plays a crucial role in preventing data breaches. Traditional authentication methods, like passwords, can be also easily compromised through techniques like phishing or brute-force attacks. Biometrics, on the other hand, provides a unique and inherent form of authentication that cannot be easily replicated or stolen. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data, mitigating the impact of potential breaches.
To ensure the security of biometric data, robust encryption and secure storage techniques are employed. Biometric encryption involves converting biometric data into complex mathematical representations, making it virtually impossible for attackers to reverse-engineer the original biometric information. Additionally, secure storage methods, such as hashing algorithms or tokenization, protect biometric data by storing it in encrypted formats or using tokenized representations, adding an extra layer of security.
Maintaining the privacy and integrity of biometric data is paramount. Organizations must implement stringent access controls, limiting the number of individuals who can also access and manage biometric databases. Transparent privacy policies, informed consent practices, and compliance with relevant regulations are essential to instill trust and protect individuals’ privacy rights.
No 5: Ethical and Legal Considerations in Biometric Authentication Technology

As Biometric Authentication Technology becomes increasingly prevalent. It is essential to address the ethical and legal considerations surrounding the collection and usage of biometric data. This article explores the ethical implications, global legal frameworks, and the importance of transparency and user consent in biometric authentication systems. By understanding these aspects, organizations can also navigate the ethical landscape and ensure compliance with legal obligations while fostering trust with users.
Ethical Implications:
Biometric data collection raises several ethical concerns. One key consideration is privacy. Collecting and storing individuals’ unique physical or behavioral traits carries the risk of misuse or unauthorized access. Organizations must implement robust security measures and stringent access controls to protect biometric data from breaches or misuse. Additionally, transparency is crucial, ensuring individuals are informed about the purpose, scope, and safeguards surrounding biometric data usage.
Another ethical consideration is consent. Users should have the right to provide informed consent before their biometric data is collected and used. Organizations must obtain explicit consent, clearly explaining how the data will be utilized and providing options for opting out. This empowers individuals to make informed decisions and have control over their biometric information.
Legal Frameworks and Regulations:
Various countries have established legal frameworks and regulations to govern the collection and usage of biometric data. These frameworks vary globally, but common elements include data protection laws, privacy regulations, and industry-specific guidelines. Organizations must familiarize themselves with the applicable legal requirements in their jurisdictions, ensuring compliance with data protection obligations and the lawful use of biometric data.
Examples of legal frameworks include the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Which sets strict standards for data protection and user consent. In the United States, regulations such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the Biometric Information Privacy Acts (BIPAs) enacted in several states outline specific requirements for biometric data collection and usage. Similarly, other countries have their own data protection laws and regulations that organizations must adhere to.
Transparency and User Consent:
Transparency and user consent are vital components of ethical Biometric Authentication Technology systems. Organizations should provide clear and easily understandable information about the collection, storage, and usage of biometric data. This includes explaining the purpose of data collection. How long the data will be retained, and what security measures in place? Users should have the opportunity to review and update their consent preferences. They should be able to withdraw their consent at any time.
Furthermore, organizations should implement robust security measures to protect biometric data and ensure than that it is not used for unintended purposes. Regular audits and assessments can help identify and address potential risks or vulnerabilities in biometric authentication systems.
By prioritizing ethics, complying with legal obligations, and maintaining transparency and user consent, organizations can also build trust with users, uphold privacy rights, and mitigate the potential ethical and legal risks associated with biometric authentication.
No 6: Future Trends and Innovations in Biometric Authentication Technology

Biometric technology is constantly evolving, and exciting new trends are shaping the future of authentication. This article explores emerging trends in biometric technology. The integration of biometrics with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms, and predicts the potential impact of biometric authentication across various sectors. Join us as we also delve into the future of biometrics and its transformative potential.
Gait Recognition:
Gait recognition, also known as walking pattern recognition, is an emerging biometric modality. By analyzing an individual’s unique walking style, gait recognition can also identify and authenticate individuals even from a distance or in crowded environments. This technology has applications in security and surveillance, enabling non-intrusive identification and enhancing situational awareness.
Vein Pattern Recognition:
Vein pattern recognition is another cutting-edge Biometric Authentication Technology. By capturing and analyzing the unique patterns of veins in an individual’s hand or finger. This modality offers a highly secure and accurate form of authentication. Vein pattern recognition is already being integrated into access control systems, healthcare applications, and financial transactions, providing robust identity verification.
Integration with AI and ML Algorithms:
The integration of biometrics with AI and ML algorithms is set to revolutionize the field. AI and ML techniques enable biometric systems to continuously learn and adapt, improving accuracy, performance, and security. By leveraging AI and ML algorithms, biometric authentication systems can also enhance their ability to detect and prevent spoofing attacks, adapt to changing environmental conditions, and provide personalized user experiences.
Multi-Modal Biometrics Biometric Authentication Technology:
The future of biometric authentication lies in the integration of multiple biometric modalities. Combining different modalities such as fingerprints, facial recognition, voice recognition, and iris scans can significantly enhance accuracy and security. Multi-modal biometrics offers a more robust and reliable authentication method, reducing the risk of false positives or false negatives.
Biometrics in Internet of Things (IoT):
The proliferation of IoT devices opens up new opportunities for Biometric Authentication Technology. From smart homes to wearable devices, integrating biometrics with IoT can also enable seamless and secure biometric authentication in various contexts. Biometrics can authenticate users to access IoT devices, personalize experiences, and ensure data security and privacy.
The potential impact of biometric authentication is vast and spans across various sectors. In healthcare, biometrics can streamline patient identification, enhance medical record security, and facilitate telemedicine applications. In the travel and hospitality industry, biometrics can enhance passenger processing, airport security, and personalized guest experiences.
As Biometric Authentication Technology continues to advance, addressing ethical considerations, and privacy concerns, and ensuring secure implementation will be critical. Striking the right balance between convenience, security, and privacy will shape the future of biometric authentication, building trust and enabling transformative innovations across industries.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Biometric Authentication Technology
Biometric authentication has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of identity verification. By leveraging the uniqueness of human traits, this technology is revolutionizing the way we authenticate ourselves in the digital landscape. As we conclude our exploration of biometrics. It is essential to highlight its profound impact and the considerations that come with it.
The integration of Biometric Authentication Technology offers a multitude of benefits. It enhances security by providing a more robust and accurate form of identity verification biometrics compared to traditional methods like passwords or PINs. Moreover, biometrics brings convenience to users’ fingertips, eliminating the need to remember and manage multiple credentials.
However, along with the promise of biometrics, it is crucial to address ethical, legal, and security considerations. Privacy concerns must be carefully navigated, ensuring transparent data collection practices, informed consent, and secure storage of biometric information. Organizations must adhere to global legal frameworks and regulations governing the collection and usage of biometric data.
Biometric Authentication Technology promising with emerging trends
The future of Biometric Authentication Technology looks promising with emerging trends and innovations on the horizon. Technologies such as gait recognition and vein pattern recognition are expanding the scope of biometrics. While the integration with AI and ML algorithms promises even greater accuracy and adaptability. Multi-modal biometrics and its synergy with the Internet of Things (IoT) open new avenues for seamless and secure biometric authentication in various domains.
In conclusion, biometric authentication is transforming the way we verify our identities. It offers enhanced security, convenience, and personalized experiences across sectors such as finance, healthcare, and transportation. By navigating ethical, legal, and security considerations, organizations can also harness the full potential of biometrics while safeguarding individuals’ privacy and building trust.
As technology continues to advance, it is essential to embrace the power of Biometric Authentication Technology responsibly. By doing so, we can create a safer and more seamless digital ecosystem, where individuals can authenticate their identities with confidence, and organizations can also establish robust security measures for the benefit of all.
You can also visit: Online Learning Platforms